
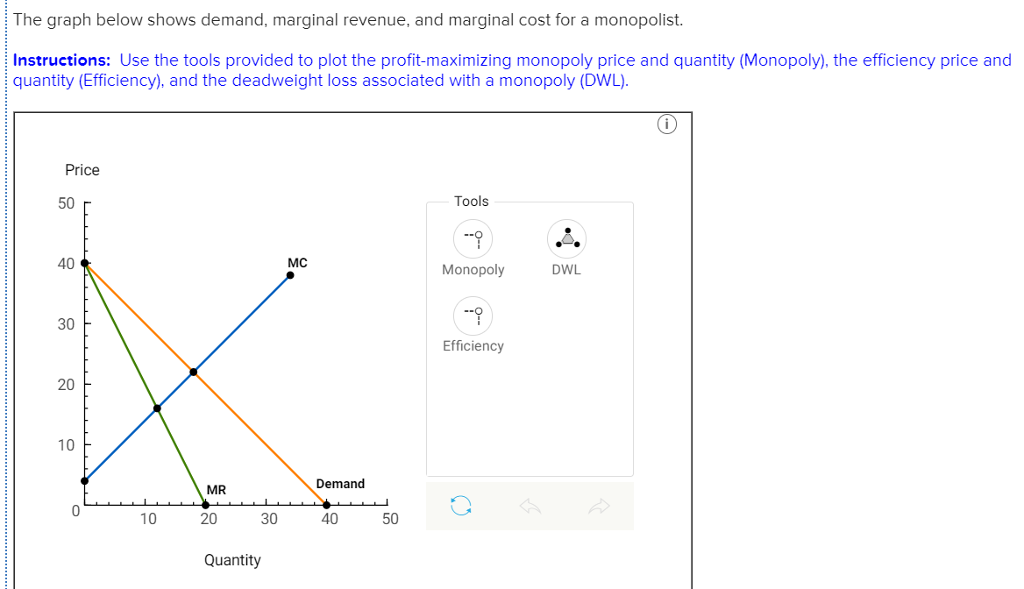
Intuit does not endorse or approve these products and services, or the opinions of these corporations or organizations or individuals. We provide third-party links as a convenience and for informational purposes only. Firm A maximizes profit by setting its marginal revenue equal to marginal cost. Readers should verify statements before relying on them. In Topic 3, we determined that the supply curve was derived from a firms Marginal Cost and that shifts in the supply curve were.
#Marginal revenue graph builder free
does not warrant that the material contained herein will continue to be accurate nor that it is completely free of errors when published. If the business drops the price from 3 to 2, total revenue decreases by 6. For example, if the business reduces the price from 7 to 6, and quantity increases to 5, total revenue increases by 2, and marginal revenue is 2. Accordingly, the information provided should not be relied upon as a substitute for independent research. Marginal Revenue Change in Revenue / Change in Quantity Sold: As you can see, the marginal revenue fluctuates. does not have any responsibility for updating or revising any information presented herein. No assurance is given that the information is comprehensive in its coverage or that it is suitable in dealing with a customer’s particular situation. Applicable laws may vary by state or locality. Additional information and exceptions may apply. theory, demand concepts, elasticity of demand, marginal cost marginal revenue, the short. This content is for information purposes only and should not be considered legal, accounting, or tax advice, or a substitute for obtaining such advice specific to your business. Managerial economics helps the management in decision making. Using the marginal cost formula, we can determine how an additional production run will impact profitability. The average cost of producing a watch in the first run is $100, but the marginal cost is the additional cost to produce one more unit. The manufacturer will want to analyze the cost of another multiunit run to determine the marginal cost. If you're producing at a quantity where marginal costs exceed marginal revenue, that negatively impacts your profitability.įor example, let’s say a company produces 5,000 watches in 1 production run at $100 apiece.
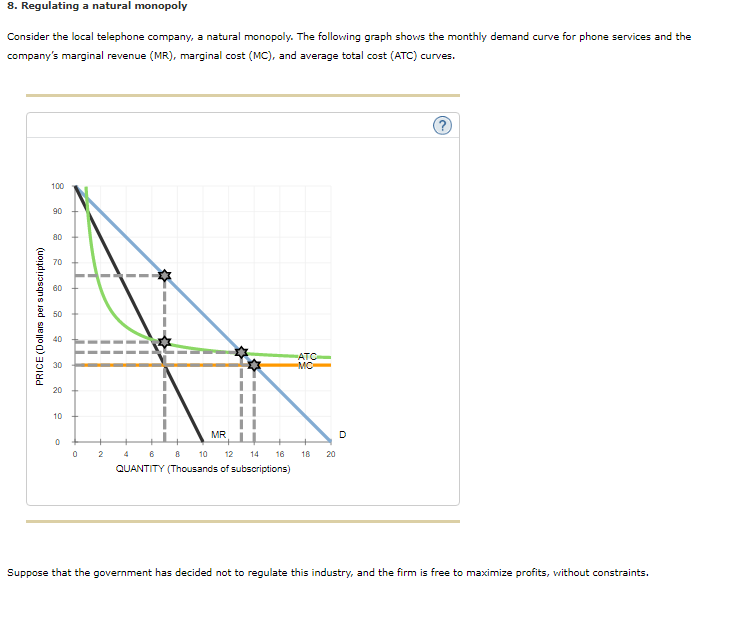
Preventing your company from losing money through loss of sales or overproduction Perfect Substitites Utility (3D) Quasilinear Utility (3D) Concave Utility (3D) MRS and Marginal Utility (3D) MRS Along an Indifference Curve (3D) Constrained Optimization.
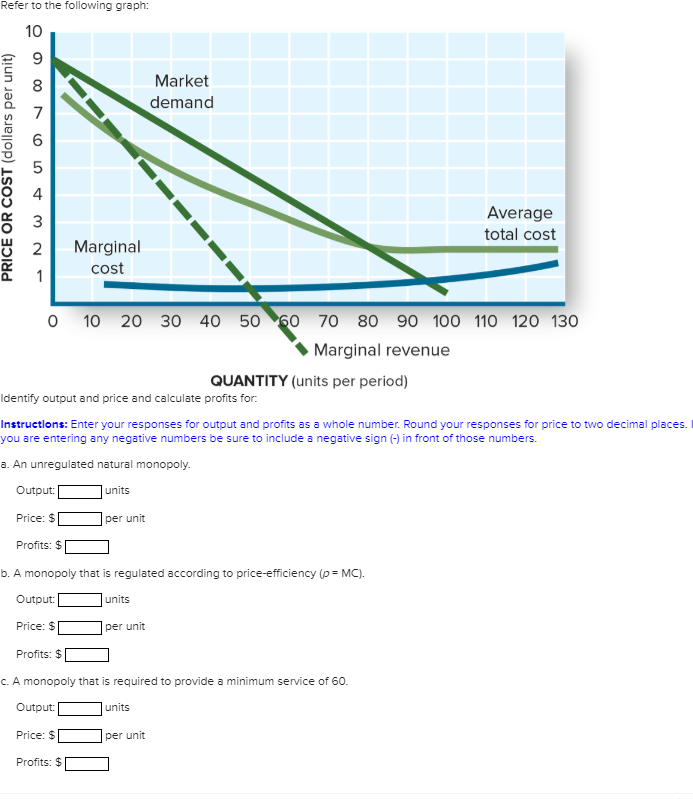
It’s the blueprint needed to find the sweet spot of effective output and can yield several other benefits, such as: Marginal cost is important because if you’re looking to maximize profits, you’ll want to plan production so that your marginal costs are equal to your marginal revenue.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
